Diagnostic imaging plays a crucial role in modern medicine, allowing healthcare professionals to visualize and diagnose various medical conditions. There are several types of diagnostic imaging techniques, each with its own unique capabilities and applications. In this post, we will explore the different types of diagnostic imaging and their significance in healthcare.
What is diagnostic imaging, and why is it important in healthcare?
Diagnostic imaging, an essential component of modern healthcare, encompasses various techniques such as X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds, enabling healthcare professionals to visualize internal structures and diagnose medical conditions. These imaging modalities play a pivotal role in early detection, accurate diagnosis, and monitoring of diseases, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes. By providing detailed insights into the body’s anatomy and pathology, diagnostic imaging facilitates personalized treatment plans and minimizes the need for invasive procedures. Moreover, it aids in guiding surgical interventions and assessing treatment effectiveness. In essence, diagnostic imaging is indispensable in improving healthcare delivery and patient care.
Diagnostic imaging refers to a variety of techniques used to create images of the inside of the body to diagnose and treat medical conditions. These images help healthcare professionals identify and evaluate abnormalities, injuries, and diseases, enabling them to make informed decisions about patient care.
X-Rays:
X-rays are a common form of diagnostic imaging that uses electromagnetic radiation to create images of the body’s internal structures. They are particularly useful for detecting bone fractures, lung conditions, and dental issues. X-rays are non-invasive and provide quick results, making them an essential tool in medical diagnostics.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scans:
CT scans utilize a combination of X-rays and computer technology to produce detailed cross-sectional images of the body. They are valuable for detecting internal injuries, tumors, and other abnormalities in organs such as the brain, lungs, and abdomen. However, CT scans expose patients to higher levels of radiation compared to other imaging techniques.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
MRI uses powerful magnets and radio waves to generate detailed images of the body’s soft tissues, organs, and blood vessels. It is particularly effective in diagnosing conditions such as brain tumors, spinal cord injuries, and joint disorders. MRI is non-invasive and does not involve ionizing radiation, making it a safer option for certain patient populations.
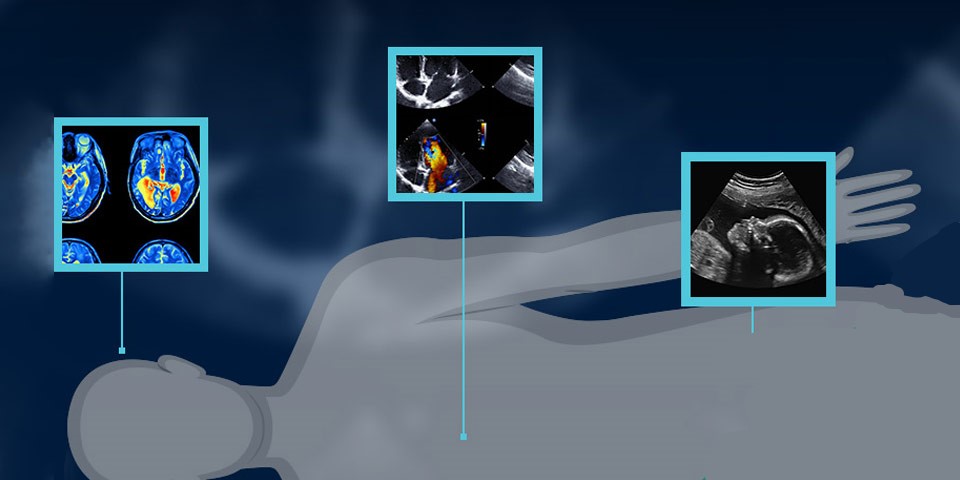
Ultrasound:
Ultrasound imaging uses high-frequency sound waves to create real-time images of the body’s internal structures. It is commonly used for prenatal screenings, evaluating the heart and blood vessels, and diagnosing conditions in the abdomen and pelvis. Ultrasound is non-invasive, portable, and does not use ionizing radiation, making it a safe and versatile imaging modality.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scans:
PET scans use a radioactive tracer to produce detailed images of the body’s metabolic processes. They are valuable for detecting cancer, assessing brain function, and evaluating cardiac conditions. PET scans provide information about the body at the cellular level, aiding in the early detection and monitoring of various diseases.
Conclusion
Diagnostic imaging encompasses a diverse range of techniques that are essential for the accurate diagnosis and management of medical conditions. Each type of imaging modality offers unique advantages and applications, contributing to the comprehensive care of patients. By understanding the different types of diagnostic imaging, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions about the most appropriate imaging technique for each patient’s needs, ultimately improving patient outcomes and quality of care.